April 28, 2023
Error analysis method under correlated noise in interferometric images
SOKENDAI Publication Grant for Research Papers program year: 2022
Takafumi Tsuku(alumnus), Astronomical Science
Estimating the statistical uncertainty due to spatially correlated noise in interferometric images
Journal: Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems publish year: 2023
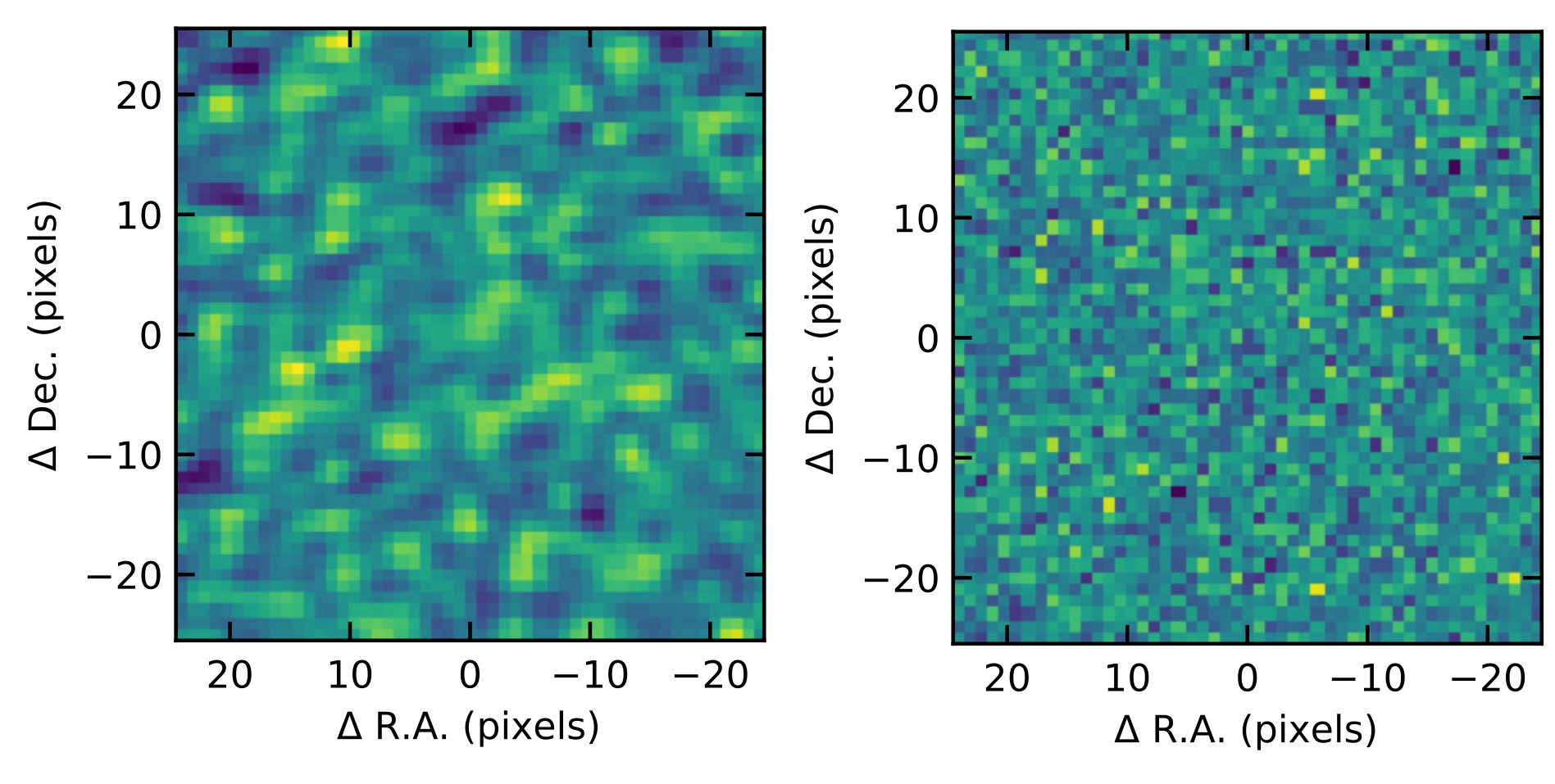
Left: Noise map with a spatial correlation between neighbouring pixels. Right: Noise map without spatial correlation between pixels. Although both noise images have the same amplitude, they look different and affect differently to the uncertainty of the results.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array(ALMA)telescope consists of 66 antennas that simultaneously observe a single target and function as a single telescope(so-called interferometric observation). ALMA has archived the highest sensitivity and resolution in the world at the observable wavebands, making significant contributions to a wide range of fields in astronomy, from galaxy formation to star and planet formation.
In scientific processes, it is crucial to estimate the uncertainty of the measurements or detected signals — how much the measured value would fluctuate due to the noise and how likely it is that the noise will produce a signal that is thought to be a discovery. In the interferometric observation, images produced by computationally synthesizing data from each antenna have noise with complex correlation patterns due to its complex image synthesis method.
To date, there have not been established methods for correctly estimating the uncertainty due to the noise having such a complex correlation pattern. In this study, we propose methods measuring the correlation pattern of noise using the autocorrelation function and estimating uncertainty for various measurements (e.g., integrated flux over some image region) using the measured autocorrelation function. We further show that the previously used approximate method greatly underestimates the uncertainty.
Many research papers using radio interferometer images did not describe how to estimate the uncertainty of their measurements. This may be because understandings of the noise and methods to estimate the uncertainty has yet to be established. This study provides answers to these questions and will facilitate the reproducibility of papers in the field. The open-source code ESSENCE: Evaluating Statistical Significance undEr Noise CorrElation, has been published along with the paper, intended for easy application by a wide range of communities.
Bibliographic information of awarded paper
- Title: Estimating the statistical uncertainty due to spatially correlated noise in interferometric images;
- Authors: Takafumi Tsukui, Satoru Iguchi, Ikki Mitsuhashi, and Kenichi Tadaki
- Journal Title: Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems
- Publication Year: 2023
- DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.JATIS.9.1.018001
Department of Astronomical Science Takafumi Tsukui(alumnus)

I am doing research on how galaxies form and evolve at Australian National University.
